What Is Three-Phase Power and How Is It Different from Single Phase?

Introduction
Electricity doesn’t flow into every building the same way. The type of power system, whether it’s single-phase or three-phase, affects how electrical load is distributed and how efficiently energy is delivered. It also determines the amount of equipment that can be supported and the stability of the supply under heavy demand.
In Singapore, most homes run on single-phase power because their needs are relatively modest. This setup provides a steady supply for typical residential consumption without unnecessary complexity. In contrast, commercial and industrial facilities often depend on three-phase power to handle larger, more complex loads without strain. It provides a steady, balanced supply of electricity to operate heavy machinery and multiple high-demand systems at the same time without overloading.
In this article, we identify what three-phase power is, how it differs from single-phase, and why the choice between them matters for everything from energy efficiency to equipment lifespan.
Key Takeaways:
- How Does Three-Phase Power Differ from Single-Phase?
Three-phase power delivers a continuous, balanced supply through three alternating currents that are 120 degrees apart. This makes it more stable and efficient than single-phase systems, which have voltage dips between cycles.
- What Are the Standard Voltages in Singapore?
In Singapore, standard voltages are 400 V between phases and 230 V between a phase and neutral. A three-phase system is ideal for commercial and industrial environments with high power demands.
- Where Is Three-Phase Power Commonly Used?
It is widely applied in industrial machinery, large commercial buildings, data centres, and factories. These settings require a stable voltage and higher load capacity to improve equipment performance and reliability.
- How Do You Choose Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power?
The decision depends on load requirements, cost considerations, and future growth plans. Single-phase systems suit most residential and low-load settings, while three-phase power benefits high-demand operations.
Overview of Three-Phase Power
What Is Three-Phase Power?
Three-phase power is a method of delivering electricity through three alternating currents, each offset by 120 degrees. This three-phase electrical system generally uses four wires: three live conductors that carry current and one neutral wire that completes the circuit. This arrangement allows for a continuous, balanced flow of electricity, unlike single-phase power, where voltage periodically drops to zero. As a result, it provides a steadier supply that can handle heavier loads more efficiently.

What are the Standard Voltages in Singapore?
In Singapore’s commercial and industrial infrastructure, three-phase systems supply 400 volts between any two phases and 230 volts between a single phase and neutral. This configuration is well-suited for environments where high power output and stability are essential.
What are the Common Applications of Three-Phase Power?
Three-phase power forms the backbone of many commercial, industrial, and high-demand environments. It provides a stable flow of electricity, making it suitable for locations that run continuously and use heavy electrical loads. It ensures power distribution efficiency to support the performance, safety, and longevity of equipment across a wide range of applications.

1. Industrial Machinery
Three-phase systems are standard in manufacturing plants and workshops. By meeting industrial power requirements, they can efficiently power motors, compressors, conveyor belts, and entire production lines. The balanced power supply reduces vibration and mechanical stress on motors, improving operational reliability and lowering maintenance costs.
2. Large Commercial Buildings
Office towers, malls, and other large facilities often rely on three-phase power along with well-planned electrical installation systems. These setups enable HVAC units, passenger lifts, and extensive lighting networks to run at the same time. The stability of this power system helps prevent outages or performance drops during peak usage hours.

3. Data Centres
In data centres, downtime is costly. Even short interruptions can lead to financial and reputational damage. Three-phase power provides the stable voltage necessary to run servers, cooling systems, and other critical IT infrastructure without interruptions. Even under heavy load conditions, it maintains consistent performance and minimises the risk of overheating, equipment strain, or unexpected shutdowns.
4. Factories
From automated assembly lines to large-scale welding equipment, factories require a high and consistent power supply. Three-phase systems can support these demands without overloading circuits, ensuring smooth and efficient production cycles.
What are the Advantages?
After looking at where three-phase power is commonly used, it’s important to understand the benefits it offers and the limitations that come with it. Having a balanced view of both can help determine whether it’s the right choice for a home, commercial space, or industrial facility.
1. Higher Efficiency
This type of power system delivers electricity in a continuous, overlapping cycle, so there are no gaps where the voltage drops to zero. This consistent supply means motors and other equipment run more smoothly, with less heat build-up and mechanical strain. As a result, it can help reduce wear and prolong service life.
2. Greater Load Capacity
Compared to single-phase power, a three-phase system can transmit more electricity using less conductor material. This makes it more cost-effective for large-scale operations in the long run, especially when powering heavy machinery, extensive lighting, or multiple high-demand systems at once.
3. Stable Voltage Levels
Because the system balances its load across three conductors, voltage fluctuations are minimised. This is especially important for sensitive devices. For instance, IT servers, laboratory instruments, or precision manufacturing tools with minor instability can lead to errors, equipment malfunctions, or production downtime.
What are the Disadvantages?
1. Higher Setup Cost
Installing a three-phase system involves more complex wiring, distribution boards, and safety components, which increases the initial investment. This higher cost may not be justifiable for smaller premises with modest power needs.
2. More Complex to Maintain
Three-phase systems are more complex than single-phase setups. They require electricians in Singapore who are trained in specialised wiring, load balancing, and safety procedures. Managing multiple conductors and working with higher voltages demands precise installation and maintenance to avoid issues. These may include voltage imbalances, overheating, or equipment damage. As these systems are often connected to sensitive or high-demand equipment, troubleshooting can be more time-consuming and requires advanced expertise.
3. Limited Residential Use
In most residential areas, the standard supply is single-phase. Accessing a three-phase system often requires special arrangements with the utility provider. This process can involve infrastructure upgrades and incur higher costs, making it impractical for typical household consumption.
Three-Phase vs Single-Phase Power: Choosing the Right One
How Does Single-Phase Differ From Three-Phase?
When deciding between single-phase and three-phase power, it’s important to look beyond the technical definitions. You should also consider how each system impacts efficiency, cost, and long-term performance.
Below are the key aspects differentiating the two options:
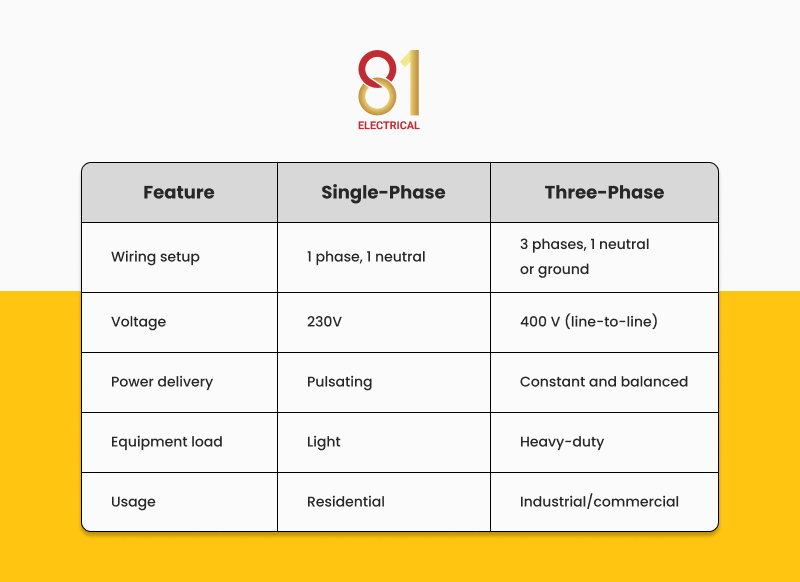
1. Power Delivery
Single-phase systems use a live (phase) wire and a neutral wire to deliver alternating current in a single sinusoidal wave. This means voltage rises and falls, creating periodic peaks and dips in power delivery. For most household appliances, this fluctuation is manageable. However, for equipment that requires a constant supply, it can lead to performance issues.
In contrast, three-phase systems deploy three live wires. Each wire carries an alternating current 120 degrees out of phase with the others. These overlapping waves ensure there is always power flowing at any given moment, providing a steady and continuous supply. This stability is particularly valuable for machinery, servers, and other equipment that cannot afford power dips.
2. Energy Efficiency
In single-phase setups, voltage dips between cycles can make high-demand appliances draw more current to maintain performance. As extra heat is generated, it reduces energy efficiency and accelerates wear on components. Over time, the lifespan of the equipment may be shortened.

On the other hand, three-phase systems maintain consistent voltage, which allows motors and heavy equipment to run more smoothly. The process requires less heat build-up and mechanical stress, saving energy and extending the equipment’s lifespan simultaneously.
3. Installation and Maintenance Cost
Single-phase power has the advantage of lower initial installation and maintenance costs, making it ideal for homes and small businesses with modest energy needs. The wiring is simpler, and servicing is more straightforward.
Three-phase systems require more complex electrical installation, including additional wiring, switchgear, and safety measures, which increases the initial cost. However, for operations with high and continuous energy demands, the efficiency and capacity of three-phase systems can offer better long-term value by reducing downtime, improving performance, and avoiding costly equipment failures.
4. Availability and Use Cases
Single-phase power is the standard in most residential areas and small commercial premises. It can reliably handle the typical electrical loads found in these settings. This includes lighting, household appliances, and small-scale air-conditioning systems. A single-phase supply provides adequate performance without the need for the higher capacity and more complex infrastructure of a three-phase system.
A three-phase system is the preferred choice for industrial and commercial electrical supplies. In environments such as factories, data centres, and large commercial buildings, equipment like industrial motors, HVAC systems, and automated machinery may all operate at the same time. A three-phase supply ensures that these loads receive a steady, balanced flow of electricity, reducing the risk of voltage drops, overheating, or equipment failure.
How to Choose Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Choosing the right power system requires looking beyond what is already installed. It’s a decision that affects how efficiently your property runs, how much you spend on energy over time, and whether you can meet future power demands.
1. Evaluate Your Electrical Load
The first step is to evaluate your electrical load. Single-phase power is generally sufficient for homes, such as HDB flats and condominiums, as well as small businesses that rely on standard lighting, appliances, and basic air-conditioning.
Three-phase power, on the other hand, is designed for environments with heavier demands. This includes large HVAC systems, industrial machinery, elevators, compressors, and data centres where continuous, high-volume electricity is essential. Through electrical load assessment, you can decide the right power system to use.
2. Compare Costs vs. Long-Term Needs
Cost is another major factor. As single-phase systems are cheaper to install and maintain, they are well-suited for low-demand settings. Meanwhile, three-phase systems can be more cost-effective over the long term in high-load environments. Although they are more expensive upfront due to the additional wiring and safety infrastructure, they can help lower operational expenses and extend equipment lifespan.
3. Check Local Availability
Availability also plays a part. In Singapore, single-phase power is the standard for most residential properties. Three-phase supply is more common in commercial buildings, industrial parks, and large landed properties, although installation may require approval from the utility provider and infrastructure upgrades. Consult a licensed electrical contractor before committing to an upgrade.
4. Plan for Future Growth
Finally, it’s important to think ahead. If you plan to expand your business or add more equipment, investing in a three-phase system early may be more cost-efficient than carrying out a full electrical overhaul later.
In summary, single-phase power is generally suitable for standard residential and light commercial use, while a three-phase system is better suited to facilities with heavy-duty machinery, high operational loads, or sensitive equipment that needs a stable power supply. A professional assessment from a licensed electrical contractor or LEW can help ensure you choose the most suitable and cost-effective system for your needs.
Should You Use Single-Phase or Three-Phase Power?
For most households, such as HDB flats, condominiums, and typical landed homes, as well as small shops or light-use warehouse units, single-phase power is more than adequate. It provides reliable electricity for everyday appliances and modest energy needs without the added cost or complexity of a three-phase system.
Three-phase power is better suited to businesses and properties that operate heavy-duty machinery, large HVAC systems, or other high-load equipment that requires a stable and continuous supply. In these environments, the added capacity and efficiency can make a significant difference to performance, operating costs, and equipment lifespan.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your current usage and your future plans. A Licensed Electrical Worker (LEW) can recommend the most appropriate and cost-effective option for your property. By making an informed decision now, you can keep your electrical system safe and efficient.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is three-phase power more efficient than single-phase?
Yes, this type of system delivers power more smoothly and efficiently, especially for large or constant loads. It reduces voltage drops and allows for smaller wiring in high-load applications.
2. Can I use a 3-phase appliance on single-phase power?
Generally, 3-phase appliances are designed to run on 400 V across multiple phases. However, some equipment may be convertible or compatible with a phase converter. Consult a licensed electrician in Singapore for more information.
3. How do I know if my property has 3-phase power?
Check your main distribution board or electricity bill for a 400 V service line. You can also consult your building’s electrical plan or hire a licensed electrical worker (LEW) to confirm.
Conclusion
When deciding between a single-phase and three-phase power, consider a few factors such as current electrical load, long-term energy requirements, installation costs, and future expansion plans. While a single-phase system may be sufficient for homes and small businesses, three-phase is often the smarter choice for operations that rely on heavy-duty machinery or multiple high-demand systems running at once. If you are unsure of which to choose, seek guidance from an experienced electrician. They can assess your setup, calculate your load requirements, and determine whether an electrical service upgrade is necessary and cost-effective.
At 81 Electrical, our licensed, experienced electricians ensure your wiring meets safety standards and operates reliably. They are well-trained to provide thorough periodic inspections and prompt rectification to keep your system in optimal condition. Whether you need advice on power system selection or complete electrical works in Singapore, we are ready to help you make the right choice for your property.
Contact us for a quote.

