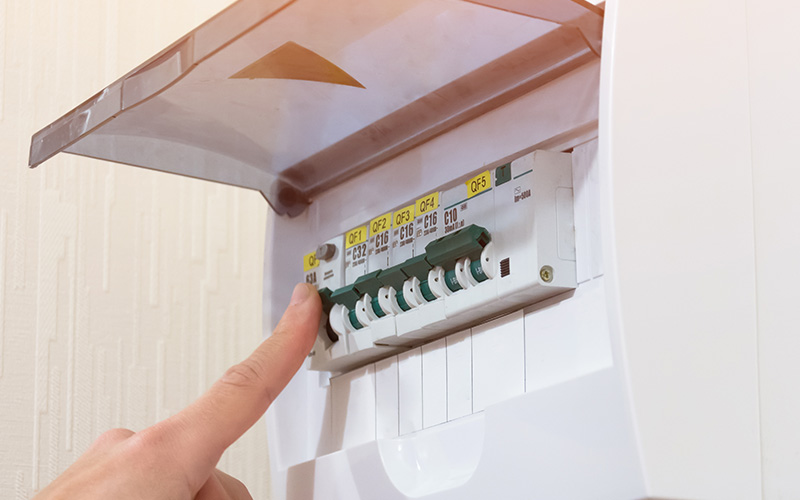
What to Do When There Is an Electrical Outage in Your HDB Flat

Introduction
Energy is a key resource for a country’s economic growth and development. In Singapore, the scarcity of natural resources necessitates the nation to rely heavily on imports to meet its domestic needs. This dependency makes the efficient use of HDB electricity particularly important, as it directly impacts both household expenses and the broader national energy strategy. As a result, power outages in Singapore are taken very seriously within the country, as they may be indicators of bad management, or failing infrastructure which can all affect our livelihoods greatly.
The energy infrastructure of Singapore mainly depends on liquefied natural gas (LNG), which constitutes approximately 95% of its electricity generation. LNG is recognised as the cleanest among fossil fuels, offering a lower carbon footprint compared to other sources such as coal and oil. The remaining 5% of Singapore’s electricity generation comes from a diverse mix of coal, oil, solar, and waste.
In response to global and local environmental concerns, Singapore is actively pursuing a transition towards more sustainable energy solutions. One of the key initiatives is the significant expansion of solar energy. The country aims to harness 1.5 gigawatt-peak (GWp) of solar energy by 2025. This target is expected to generate sufficient power for around 260,000 households annually.
Solar energy is an essential element in Singapore’s strategy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By increasing the adoption of solar technology, Singapore hopes to enhance energy security and contribute to the global effort against climate change.
Understanding Electricity in Singapore
How is Electricity Distributed in Singapore
Singapore’s electricity industry has undergone a major transformation over the years, adapting to the growing demands for reliability, affordability, and sustainability. Singapore Power Limited (SP Group), a state-owned entity, is responsible for the domestic distribution of electricity and gas.
A Brief Overview of Power Generation in Singapore
Electricity generation in Singapore is managed by various power generation companies, each owning and operating their power plants. The national power grid, operated by SP Group’s SP PowerGrid, delivers electricity to consumers islandwide.
Structure of the Electricity Market
Singapore’s electricity market is divided into the wholesale and retail sectors. In the wholesale electricity market, power generation firms place a bid every half-hour to sell their electricity in bulk. The prices in this market fluctuate based on the principles of demand and supply.
The Evolution of the Retail Electricity Market
Previously, SP Group was in charge of bulk purchases and electricity distribution. However, this process saw a shift after the launch of the Open Electricity Market (OEM). Since 2001, the Energy Market Authority (EMA) has progressively opened the retail electricity market to competition.
The entry of new competitors has driven greater innovation in the market. Retailers now offer a range of plans tailored to different consumer needs, with corresponding electricity rates. This liberalisation has also led to more choices, greater flexibility, and competitive pricing.
Continuity Amidst Change
Despite the changes introduced by the OEM, key aspects of Singapore’s electricity market, like the electricity sources and the delivery network, remain unchanged. SP Group continues to manage the national power grid, ensuring that all consumers receive a reliable electricity supply.
Commitment to Sustainability
Alongside these market developments, Singapore is committed to maintaining the availability and affordability of energy while advancing sustainability. The country continually explores and invests in cleaner energy sources and innovative technologies to lessen its environmental impact.
Electricity Grid in Singapore
Singapore’s electricity grid is renowned for its reliability and robustness, given its advanced technologies integrated across its generation and transmission network. The extensive transmission and distribution infrastructure covers systems operating at 400kV, 230kV, 66kV, 22kV, and 6.6kV. Additionally, more than 15,000 kilometres of cables stretch across the island. One of the most distinctive features of Singapore’s power system is its broad deployment of underground cabling, coupled with the progressive integration of smart grid technologies.
Advanced Infrastructure and Smart Grid Integration
Evolving from traditional electricity grids, smart grids are enhanced by sophisticated communication networks that overlay the conventional infrastructure. These grids guarantee energy security, reliability, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
SP PowerGrid has been progressively adopting smart grid technologies in Singapore to boost the efficiency and resilience of the network. Initiatives include self-monitoring systems and online condition monitoring using network-wide sensors. Besides, the use of network mesh topology, adaptive protection schemes, and semi-automated self-healing network restoration features has further improved the grid’s performance.
Thanks to substantial investments made by utilities and energy providers in reliability measures, sophisticated monitoring systems, and preventative maintenance, power failures in Singapore have become less severe. Nonetheless, factors such as extreme weather conditions, equipment failure, or unforeseen incidents can still lead to power disruption.
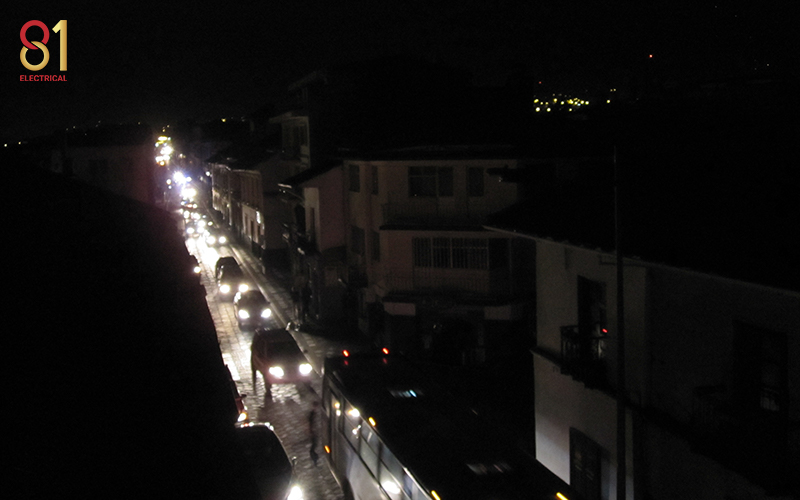

Electrical Outages: Why and What to do
Typical Electrical Loading Capacity in HDB Flats
Understanding the electrical system in your HDB flat is crucial for managing and preventing potential disruptions. In this section, we will explore the typical HDB electrical loading capacity, the role of the Consumer Unit, and the steps to take during an electrical outage.
1. Single-Phase Power Supply
Most HDB flats in Singapore are installed with a single-phase system. It can sustain the needs of an average household, powering daily essentials such as lighting, appliances, and electronic devices.
2. Load Capacity
The typical electrical circuit in an HDB flat is rated at 40 amps with a consumption capacity of 220 ampere-hours. This load capacity is designed to support common household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, without overloading the system.
3. Electrical Circuits
HDB flats are equipped with multiple electrical circuits to manage the electrical loading effectively. These circuits mitigate overloaded risks and lessen the occurrence of electrical outages or fires.

4. Consumer Unit
The Consumer Unit is one of the most critical components of an HDB flat’s electrical system. Typically housed in a metal enclosure, the Consumer Unit is installed by a licensed electrician to operate as the home’s electrical distribution board. It contributes to HDB electrical safety by regulating the distribution of power across various circuits. The Consumer Unit generally includes:
Double-Pole Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
Connected directly to the main power supply, double-pole MCBs protect circuits from high currents that exceed a specific limit. When this limit is surpassed, these breakers will trip to interrupt the circuit and prevent potential hazards. MCBs operate on a thermal principle and are usually rated at 100 amps.
Single-Pole Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
These MCBs are linked to different circuits throughout the house. They provide additional protection by ensuring the swift management of any overcurrent in individual circuits.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
RCCBs are often set to trip at leakage currents between 10 mA and 30 mA. Essential for detecting earth leakage currents, RCCBs continuously monitor the current entering and leaving a device. If there is any discrepancy or a possible earth leakage, these breakers will trip the circuit to prevent electric shocks.
Key Difference of MCBs and RCCBs
While both circuit breakers are integral to your home’s safety, they serve distinct purposes. MCBs are primarily designed to handle issues related to circuit overloads. On the other hand, RCCBs prevent electric shocks by detecting discrepancies in the current. These are some of the power failure solutions a Singaporean household should be aware of.
What You Should Know About Electrical Load
Electrical load refers to the total demand for electricity within an HDB, covering all appliances, devices, and systems that require power. Read on to discover more about electrical load management in HDB flats.
The Importance of Electrical Load Management
Proper electrical load management ensures the total electricity demand stays within the fixed limits of the system to minimise electrical hazards. It also guarantees the functionality of household appliances and devices to maintain a reliable power supply for users.
Determining Electrical Load in HDB Flats
The electrical load capacity in HDB flats can vary depending on the age and size of the flat. Here’s a closer look at how these factors influence the electrical load:
(i) Older Flats
Many older HDB flats have undergone upgrades through HDB’s Main Upgrading Programme. This includes rewiring, new distribution board installation, as well as the addition of components like a 40-amp main switch, 15-amp power points, and light switches. All of these are designed to boost the flat’s power capacity.
(ii) Newer Flats
For newer HDB flats, they usually come with higher electrical load capacities from the outset. This allows them to accommodate the simultaneous use of heavy-duty appliances to fulfil the demands of contemporary living.
Consequences of High Electrical Load
(i) Increased Power Consumption
As the demand for electricity increases, so does power consumption. This may drive up electricity bills, impacting overall household budgets over time.
(ii) Risk of Power Trips
When the electrical load exceeds its capacity, a power trip takes place. The system automatically shuts down to protect itself from overloading.
Electrical Outages vs. Power Disruptions
1. Electrical Outages (Power Failures)
An electrical outrage occurs when there is a complete loss of electrical power supply to an end user. In simpler terms, it means the electricity provided to your home has been entirely cut off.
Common Causes:
Short Circuit
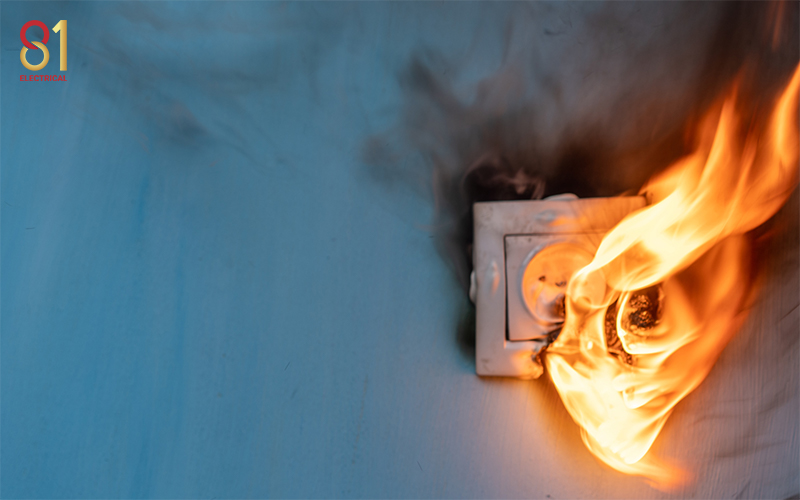
A short circuit happens when an electrical current deviates from its intended path within a circuit, causing an excessive flow of current. This can cause substantial damage to the circuit and, in severe cases, may even result in fires or explosions.
Overloading
When an electrical circuit carries more current than it is designed to handle, it triggers overloading. This excessive load can cause the circuit to overheat and escalate to potential hazards.
Blackouts
Blackouts are a severe form of electrical outage where the power supply is completely lost. The restoration time for blackouts can vary depending on the complexity of the issue that caused the outage.
2. Power Disruptions
Unlike complete outages, power disruptions involve intermittent or unstable electrical supply. In such cases, power is not entirely lost but is instead unstable or fluctuates. It may affect the normal operation of electrical devices, causing temporary malfunctions in electrical appliances or the dimming of lights.
Common Causes:
Power disruptions are often due to fluctuations in the power supply or temporary issues within the electrical network, such as momentary faults or voltage drops.
What to Do During an Electrical Outage
Even with advanced safety measures in place, electrical outages may still happen. Stay calm and take the following steps when you experience one:
1. Confirm the Power Outage
The first step is to determine whether the power outage affects a broader area. You may inspect your main electrical panel to see if any circuit breakers have tripped. If a breaker is off, reset it after disconnecting devices on that circuit. Seek professional assistance just in case the issue persists.
2. Contact Your Utility Provider
Once you’ve confirmed the electrical outage, the next step is to inform your local utility provider. Stay tuned for their updates on the situation and an estimated time for restoring power.
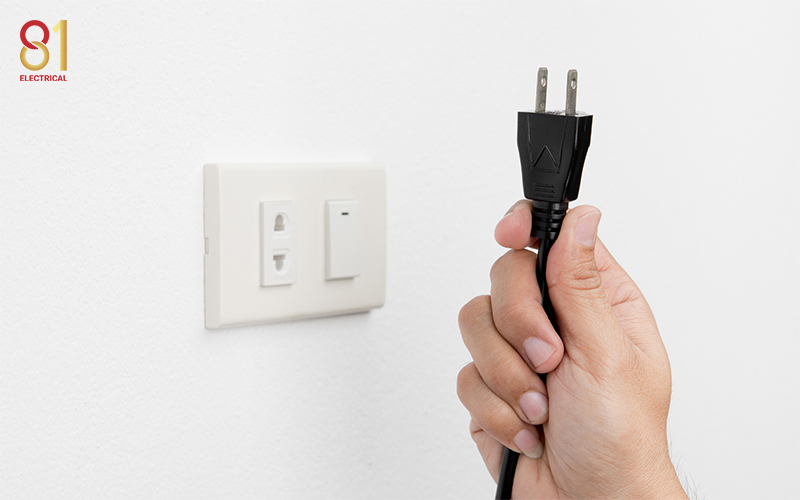
3. Unplug Appliances
Disconnect sensitive electronics like TVs, computers, and kitchen appliances to prevent damage from power surges when electricity returns. The key is to avoid overloading circuits once power is back.

4. Use Safe Lighting
Instead of using candles, it is safer to choose flashlights or battery-operated lanterns for illumination. Alternatively, you should consider deploying light bulbs with built-in batteries for added convenience.
5. Follow Generator Safety Protocols
If you’re using a generator to power your home during the outage, follow these safety guidelines:
- Never operate a generator in enclosed spaces as this can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Connect the generator directly to appliances to avoid overloading.
6. Maintain Communication
Staying informed during an electrical outage is crucial, especially if it’s prolonged. Some useful communication tools that come in handy include battery-operated or wind-up radios, and walkie-talkies.
Minimising the Risks of Electrical Outage With Proper Electrical Wiring Installation
Investing in proper electrical wiring installation in Singapore is a proactive approach to stable power supply. Here’s how it provides you peace of mind:
1. Enhanced Stability and Performance
Quality electrical installation and maintenance translates to fewer unexpected electrical outages and a lower likelihood of electrical emergencies. Moreover, a well-maintained system ensures efficient operations, minimising strain on the electrical infrastructure for longevity.
2. Improved Safety
Using high-quality materials and adhering to stringent safety standards during electrical wiring installation protects your home against potential electrical hazards. Durable, high-grade materials are less prone to degradation from factors like heat, moisture, and physical stress. Meanwhile, safe wiring practices, such as correctly sizing wires and conducting secured connections, are vital in effectively managing electrical loads throughout your home.
3. Reduced Maintenance Issues
Wiring systems that undergo regular inspections, updates, and maintenance are less likely to trigger electrical problems. To extend the lifespan of your electrical system, hire professional technicians for safe installation and thorough inspections. This proactive approach helps identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate.

Frequently Asked Questions
1.When should I contact the authorities or emergency services during an electrical outage?
When the outage is accompanied by a fire, an electrical hazard, or a risk to your safety or health. You should also make immediate reports to the relevant authorities if you suspect damage to the electrical system or see downed power lines.
2. How can I prevent short circuits in my electrical system?
Make sure your electrical wiring is in good condition and not damaged. Avoid using damaged or faulty electrical appliances and keep all connections properly insulated. It is best to entrust a licensed electrical service provider in Singapore to perform regular inspections.
3. What should I do if I suspect an issue with the electrical wiring in my flat?
Immediately stop using affected appliances and avoid any further tampering. Contact a licensed electrician to inspect and repair the wiring.
Conclusion
Electrical safety should be a priority for every home as it directly impacts the functionality and safety of your home. For HDB flats, a stable and efficient electrical system promises comfort and peace of mind. By staying informed about potential problems and employing regular system upkeep, you can protect your home from common electrical faults.
Choose 81 Electrical for Dependable Electrical Wiring Solutions
Based in Singapore, 81 Electrical provides a range of comprehensive electrical services. Our technicians are well-trained in conducting residential wiring and installations, electrical system maintenance, as well as inspections and testing. Count on our licensed and experienced electricians for top-notch solutions that meet all safety standards.
Schedule your consultation with us today.

